3B - Geological Setting
Click on map to see larger image
Rationale:
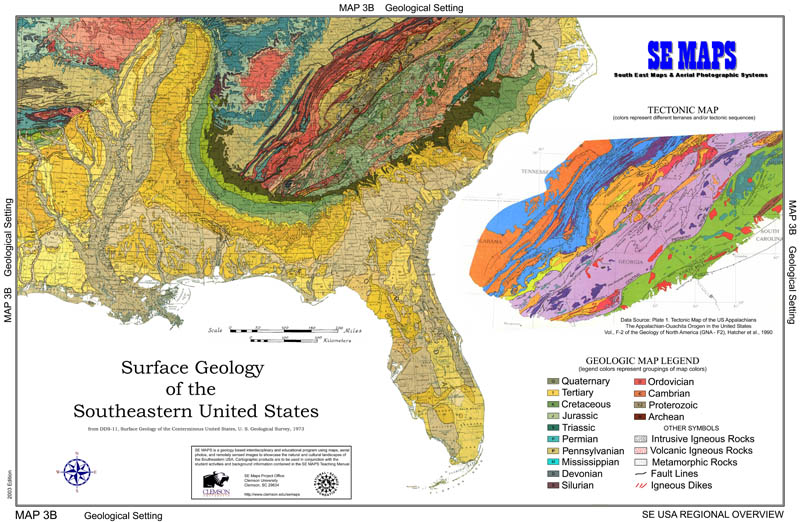
The geological makeup of a region is the single most important determining factor of how a particular landscape will develop through time. Areas underlain by igneous and metamorphic crystalline rocks tend to be the most resistant to erosion while sedimentary rocks can vary greatly in their hardness and durability. Streams cut through younger rock layers to expose older, deeper layers along the sides or bottoms of valleys. Different ages and types of rock tend to contain different fossil assemblages and mineral resources. This information can be used to infer original environments of deposition and to generate paleogeographic maps for specific geologic time periods. Occurrences of major rock units can be correlated over wide areas to make predictions about where particular fossils or mineral resources may be found. Tectonic maps divide the region into different segments based on characteristically different terranes, regions of land that contain rocks with a similar geologic history.
Themes
|
Content Outline
|
Activity TitlesAll activities include
|

|